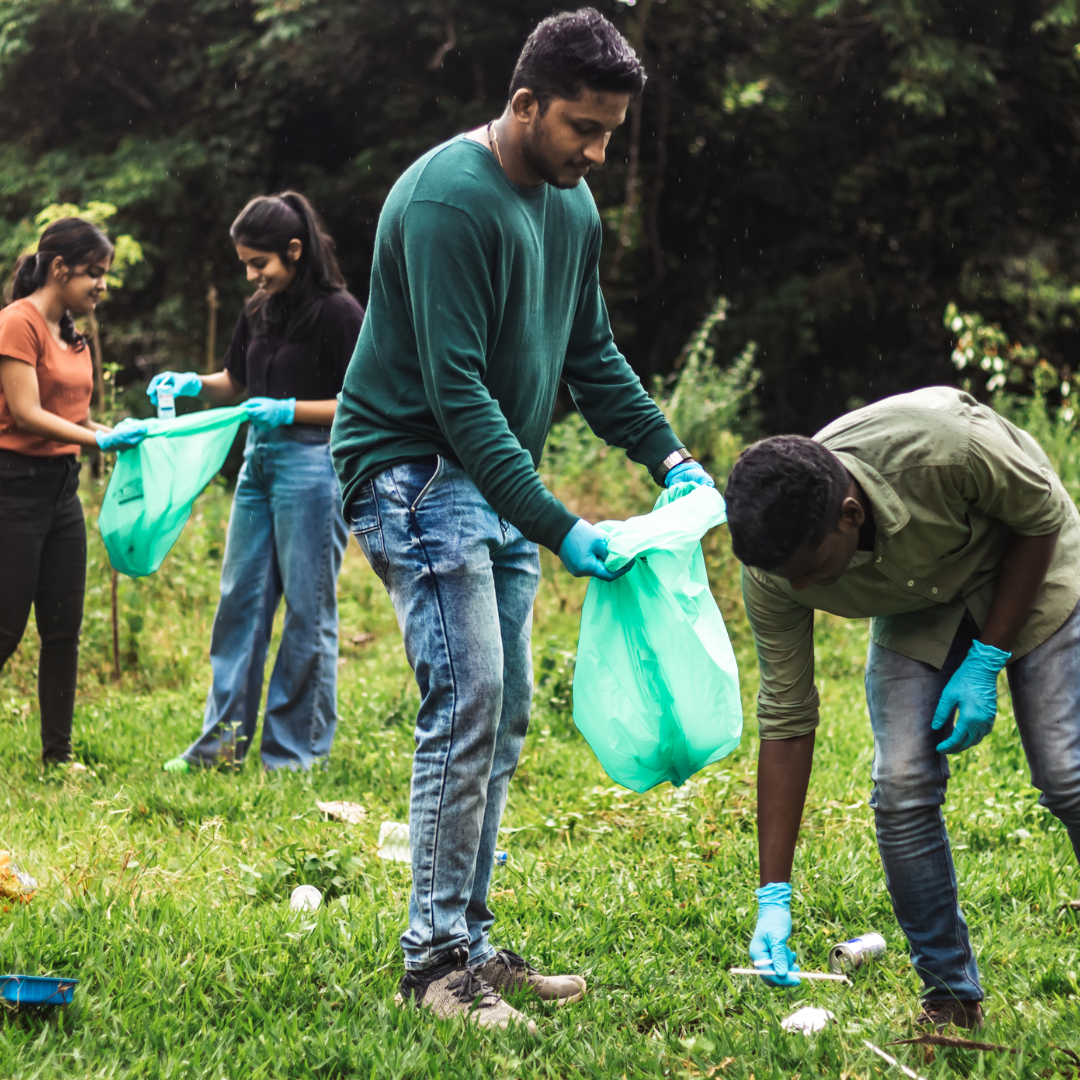
SAVE OUR BEAUTIFUL PLANET
At the heart of innovation and sustainability, our journey began with a vision to transform the polymer industry.
REDUCE
REUSE
RECYCLE
SAVE EARTH
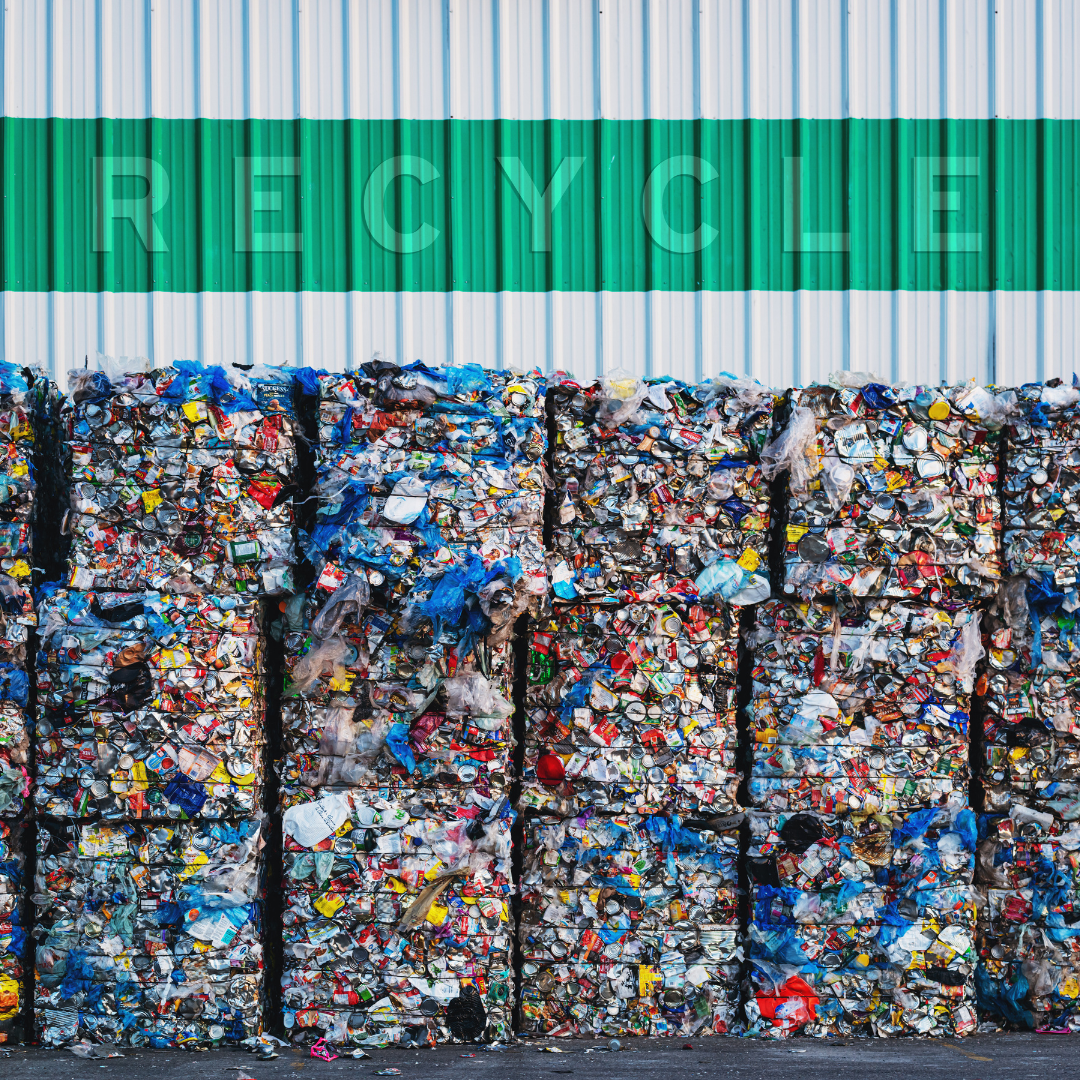

Join Over 200k People Making a Difference
Sustainability in Polymer Manufacturing
In a polymer manufacturing company, sustainability focuses on reducing environmental impact and promoting responsible use of resources. By integrating sustainable practices, the industry can contribute to a more eco-friendly and efficient production process.
- Eco-Friendly Materials
- Energy Efficiency
- Waste Management
- Water Conservation
- Green Chemistry
- Lifecycle Design
- Sustainable Sourcing
- Pollution Control
Volunteer! There Are So Many Ways to Lend a Helping Hand
Government Acts Supporting Sustainability
Government acts and regulations play a crucial role in promoting sustainability within the polymer manufacturing industry by setting standards and encouraging eco-friendly practices.
- Environment Protection Act, 1986
- Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016
- Energy Conservation Act, 2001
- Hazardous Wastes Management Rules, 2016
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)

METHODS OF RECYCLING
PCR (Post-Consumer Recycled) Method:
- Source Material: Collected from end-users or consumers after product use (e.g., plastic bottles, containers).
- Collection: Involves curbside recycling programs, drop-off centers, and reverse logistics.
- Sorting: Materials are sorted by type (e.g., PET, HDPE) to ensure high-quality recyclate.
- Cleaning: Thorough cleaning of collected materials to remove contaminants like labels, food, or chemicals.
- Shredding: The cleaned plastics are shredded into small flakes or pellets.
- Melt Processing: The shredded materials are melted and reformed into granules or pellets for reuse in manufacturing new products.
- End Products: Primarily used for non-food contact applications or downcycled into lower-grade products (e.g., packaging, textiles).
- Sustainability Impact: Reduces reliance on virgin plastic, decreases landfill waste, and lowers carbon emissions.
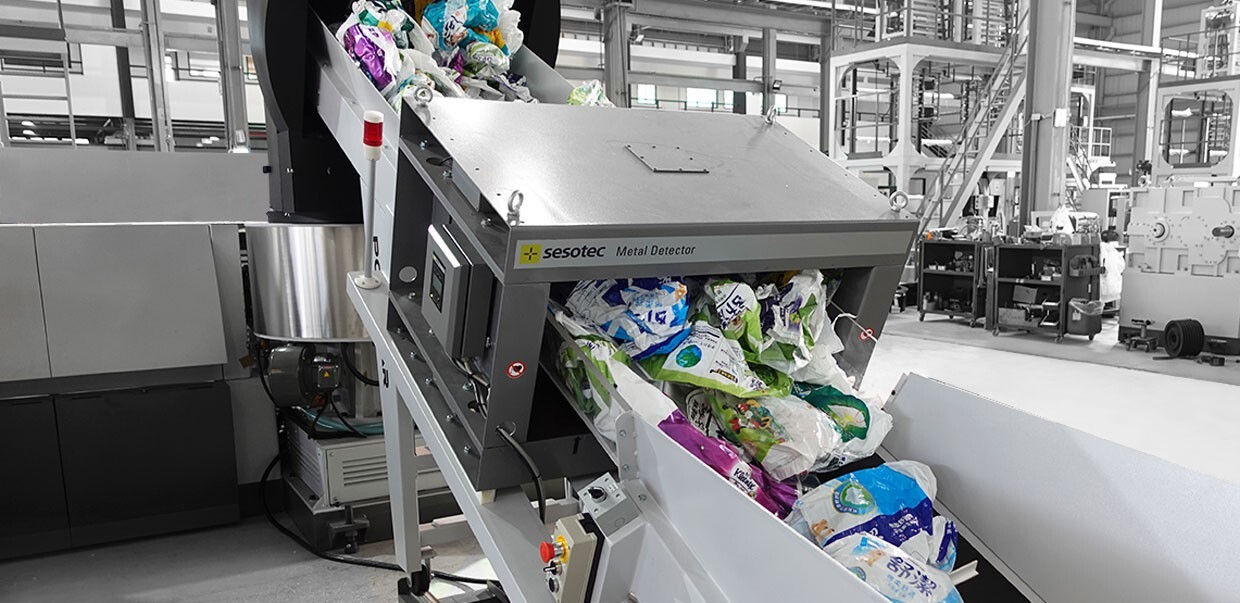
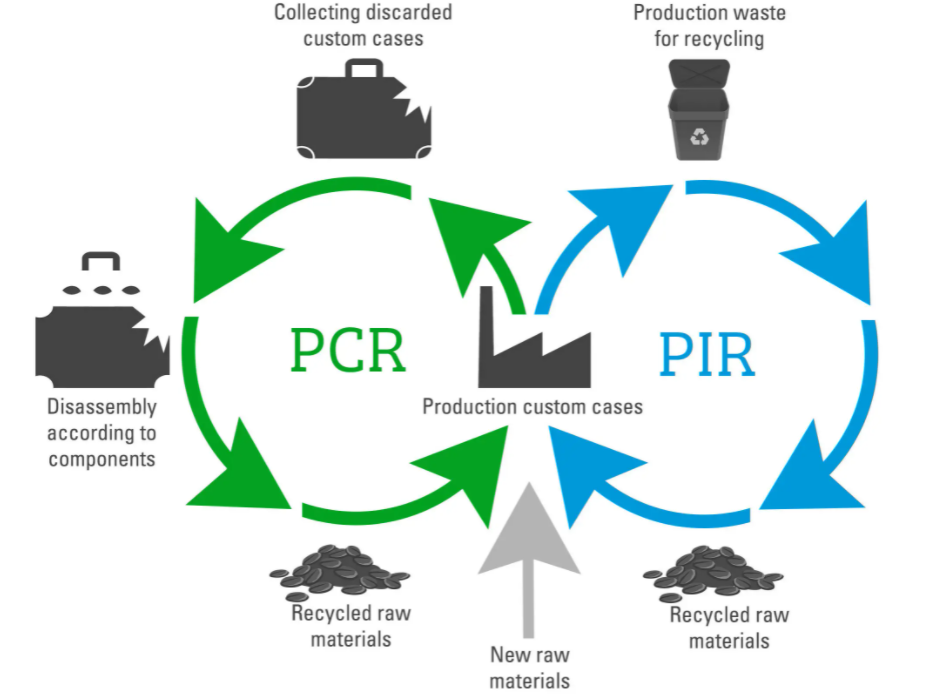

PIR (Post-Industrial Recycled) Method:
- Source Material: Comes from industrial waste during the manufacturing process (e.g., scrap material, off-cuts).
- Collection: Gathered directly from factories or production facilities as part of their by-product management.
- Sorting: Materials are sorted by type to maintain quality and consistency.
- Processing: The waste is often in better condition (since it hasn’t been used by consumers), requiring less intensive cleaning and processing.
- Reintegration: The recycled material is reintegrated directly into the production cycle, often blended with virgin polymers to maintain desired material properties.
- End Products: Used in various applications, such as packaging, automotive parts, or construction materials.
- Sustainability Impact: Helps reduce industrial waste and improves the circularity of manufacturing processes.
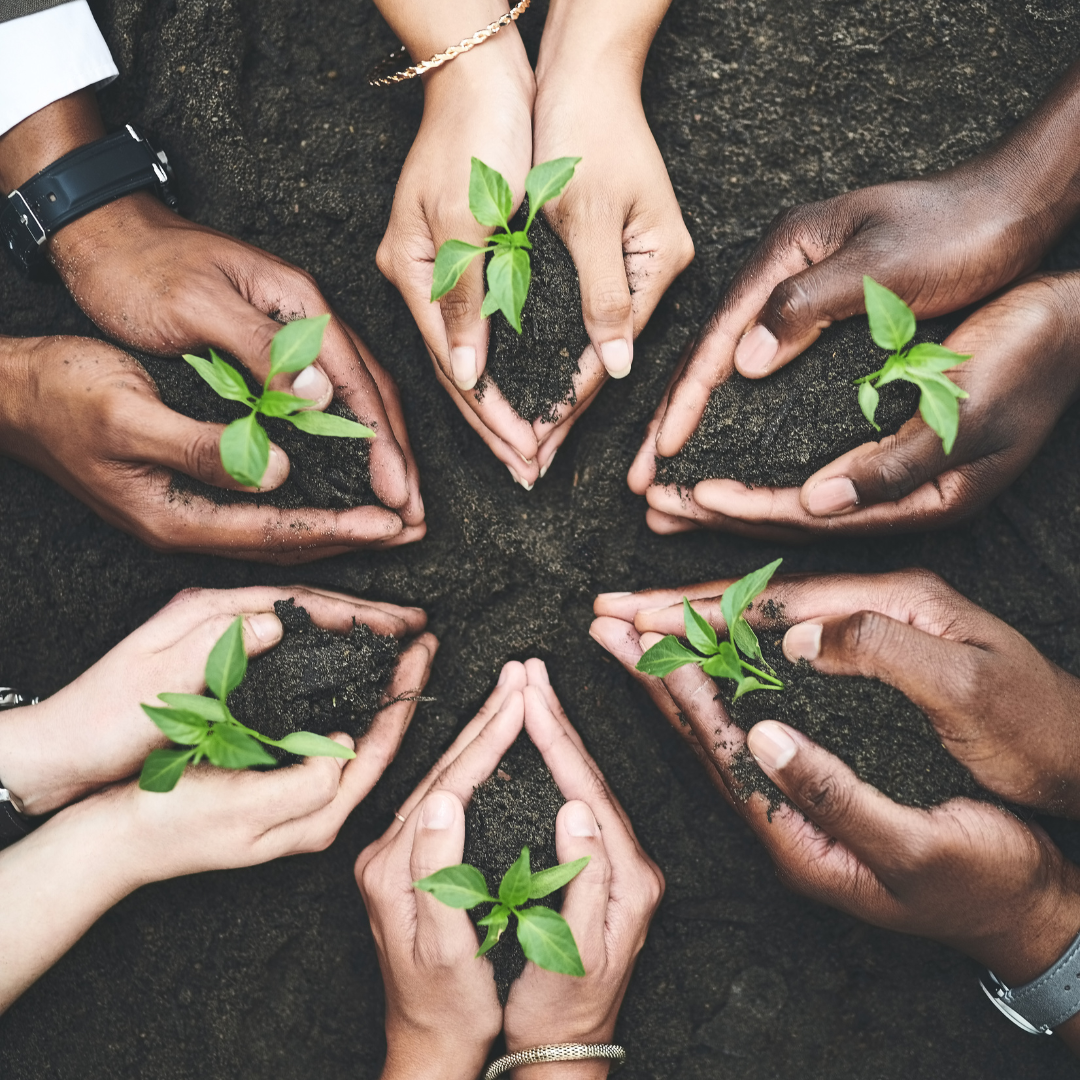
METHODS OF SUSTAINABILITY

DOING PLANTATIONS

SAVING WATER CONSERVATION
GREEN ENERGY CONSERVATION
SOLAR ENERGY CONSERVATION

WIND ENERGY CONSERVATION


